Refractive errors occur when the eye cannot properly bend (refract) light to focus on the retina, leading to blurred vision. This happens due to abnormal corneal curvature, axial length variation, or lens defects.
🔹 Types of Refractive Errors:
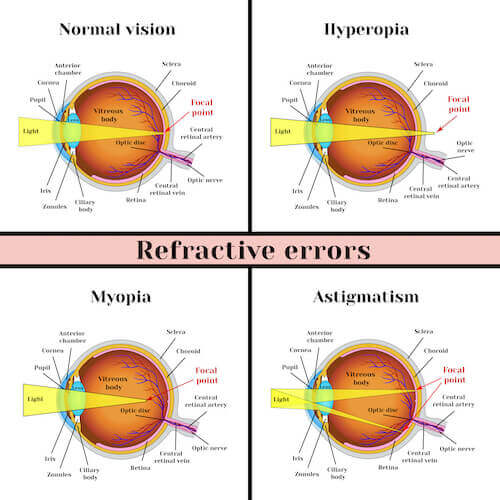
- Myopia (Nearsightedness)
- Hyperopia (Farsightedness)
- Astigmatism (Irregular Corneal Shape)
- Presbyopia (Age-Related Lens Stiffening)
🔹 Correction Methods:
- Glasses (Convex/Concave Lenses)
- Contact Lenses
- Refractive Surgeries (LASIK, PRK, ICL, etc.)
I. Understanding Refractive Errors in Detail
1. Myopia (Nearsightedness)
🔹 Definition: Light rays focus in front of the retina due to a longer eyeball or steep cornea.
🔹 Symptoms:
- Blurred distance vision
- Clear near vision
- Eye strain, headaches
🔹 Causes:
- Genetics (hereditary)
- Prolonged near-work (e.g., reading, screens)
- Axial elongation of the eyeball
🔹 Correction by Lenses:
- Concave (Diverging) Lens (-ve power)
- Moves focal point back to the retina
🔹 Advanced Correction:
- Orthokeratology (Ortho-K): Special lenses worn overnight to reshape the cornea.
- LASIK, PRK: Laser surgery to reshape corneal curvature.
2. Hyperopia (Farsightedness)
🔹 Definition: Light rays focus behind the retina due to a short eyeball or flat cornea.
🔹 Symptoms:
- Blurred near vision, sometimes distance too
- Eye strain, headaches
- Difficulty in reading
🔹 Causes:
- Short axial length of the eye
- Flat cornea or lens insufficiency
🔹 Correction by Lenses:
- Convex (Converging) Lens (+ve power)
- Moves focal point forward onto the retina
🔹 Advanced Correction:
- Hyperopic LASIK (reshapes the cornea to steepen it)
- Implantable Contact Lenses (ICLs)
3. Astigmatism
🔹 Definition: Irregular corneal shape causes multiple focal points, leading to distorted vision.
🔹 Symptoms:
- Blurred or distorted vision at all distances
- Eye strain, headaches
- Difficulty seeing fine details
🔹 Causes:
- Corneal asymmetry
- Genetic predisposition
- Post-surgical or traumatic corneal scars
🔹 Correction by Lenses:
- Cylindrical Lenses (Toric Lenses) to correct meridional distortion
- Soft Toric Contact Lenses
🔹 Advanced Correction:
- LASIK/PRK (reshapes the cornea symmetrically)
- Corneal Cross-Linking (for progressive cases like Keratoconus)
4. Presbyopia (Age-Related Lens Stiffening)
🔹 Definition: Loss of accommodation due to aging, making near vision difficult.
🔹 Symptoms:
- Difficulty in reading fine print
- Holding objects farther away to see clearly
- Headaches and eye strain
🔹 Causes:
- Age-related hardening of the crystalline lens
- Reduced ciliary muscle function
🔹 Correction by Lenses:
- Bifocal/Progressive Lenses
- Reading Glasses (+ve lens for near work)
- Multifocal Contact Lenses
🔹 Advanced Correction:
- Monovision LASIK (one eye corrected for near, the other for distance)
- Presbyopic IOLs (Multifocal intraocular lenses post-cataract surgery)
II. Optical Corrections: Understanding Lenses
Table 1: Lens Types and Their Uses
| Refractive Error | Lens Type | Effect on Light Rays | Example Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Myopia | Concave (-ve) | Diverges rays | -1.50D |
| Hyperopia | Convex (+ve) | Converges rays | +2.00D |
| Astigmatism | Cylindrical (Toric) | Corrects meridional error | -1.75D x 180° |
| Presbyopia | Bifocal/Progressive | Near & Distance zones | Add +2.50D |
III. Modern Refractive Correction Techniques
Table 2: Surgical & Non-Surgical Corrections
| Correction Method | Indication | Procedure | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glasses | All refractive errors | External lenses | Cheap, easy, non-invasive |
| Contact Lenses | Myopia, Hyperopia, Astigmatism | Placed on cornea | Better peripheral vision |
| LASIK/PRK | Myopia, Hyperopia, Astigmatism | Corneal reshaping by laser | Permanent correction |
| ICL (Implantable Lens) | High Myopia, Hyperopia | Lens implanted inside eye | Reversible, preserves cornea |
| Orthokeratology (Ortho-K) | Myopia Control | Worn at night to reshape cornea | Non-surgical, reversible |
IV. Clinical Assessment of Refractive Errors
1. Subjective Refraction
- Trial Lenses: Patient tested with different lenses to improve vision.
- Phoropter Test: Automated test to determine best corrective lens.
2. Objective Refraction
- Retinoscopy: Measures light reflex from retina.
- Autorefractor: Quick and automated measurement of refractive error.
3. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
| Test | Purpose | Used for |
|---|---|---|
| Corneal Topography | Maps corneal curvature | Astigmatism, Keratoconus |
| Aberrometry | Analyzes higher-order aberrations | LASIK Evaluation |
| OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) | Retinal & corneal assessment | High Myopia, Presbyopia |