Trividha Pariksha is the fundamental diagnostic approach in Ayurveda, consisting of Darshana (Observation), Sparshana (Palpation), and Prashna (Interrogation). This structured process helps clinicians in quick and accurate disease diagnosis.
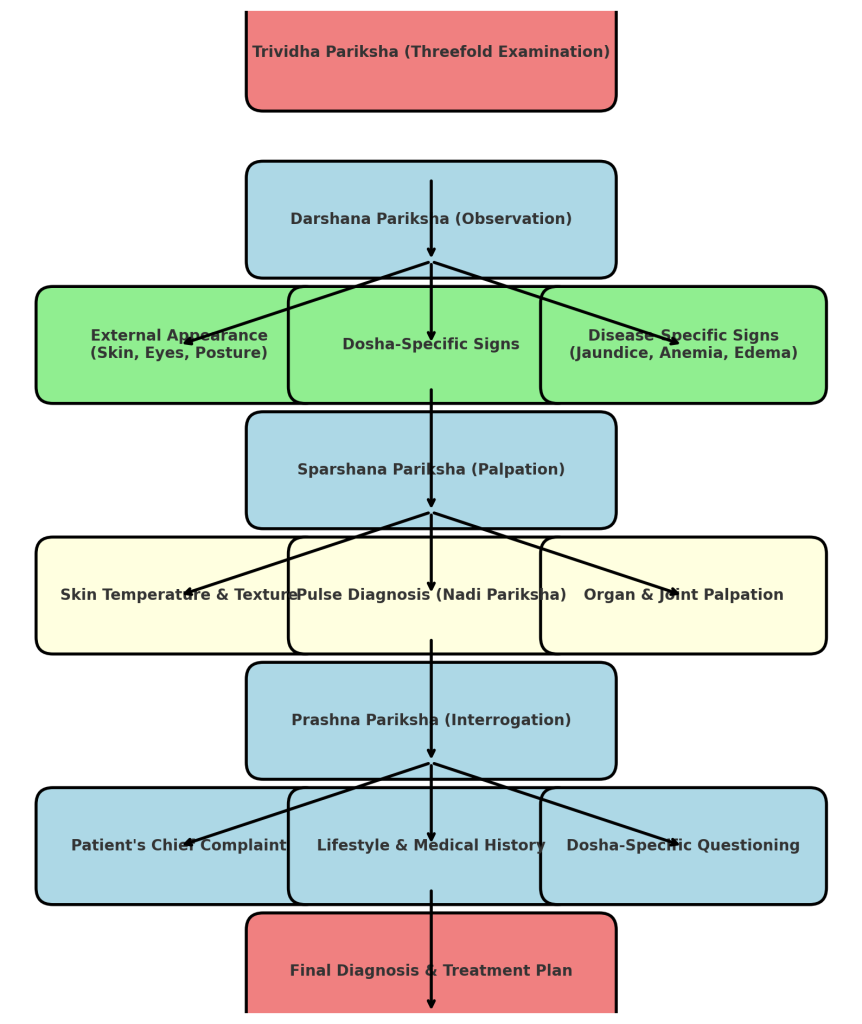
Stepwise Clinical Flowchart for Trividha Pariksha
1. Darshana Pariksha (Observation-Based Diagnosis)
🔍 Step 1: General Patient Assessment
- Observe posture, gait, body structure.
- Identify signs of weakness, swelling, or deformities.
- Check skin texture, complexion, and any visible lesions.
🔬 Step 2: Dosha-Based External Examination
- Vata Dominance: Dry skin, thin body frame, restless movements.
- Pitta Dominance: Red skin, excessive sweating, inflamed areas.
- Kapha Dominance: Oily skin, sluggish movements, excess weight.
👁 Step 3: Disease-Specific Observation
- Jaundice: Yellow eyes and skin.
- Anemia: Pale conjunctiva and lips.
- Edema: Swollen legs, pitting sign.
- Skin Disorders: Rash, discoloration, scaling.
📊 Clinical Benefit: Quick identification of external disease markers and systemic imbalances.
2. Sparshana Pariksha (Palpation-Based Diagnosis)
✋ Step 1: Skin & Temperature Assessment
- Cold & dry skin → Vata disorder.
- Warm & red skin → Pitta disorder.
- Cool & moist skin → Kapha disorder.
👐 Step 2: Pulse Examination (Nadi Pariksha)
- Vata Pulse: Irregular, thin, fast.
- Pitta Pulse: Strong, bounding, warm.
- Kapha Pulse: Slow, deep, steady.
🤲 Step 3: Abdominal Palpation (Udara Sparshana)
- Hard, distended abdomen → Kapha accumulation.
- Tender, burning abdomen → Pitta imbalance.
- Tympanic sound, gurgling → Vata imbalance.
🤕 Step 4: Joint & Muscle Palpation (Sandhi & Mamsa Sparshana)
- Pain with cracking → Vata arthritis.
- Red, inflamed joints → Pitta arthritis.
- Swollen, stiff joints → Kapha arthritis.
📊 Clinical Benefit: Confirms doshic involvement, helps in pain and organ assessments.
3. Prashna Pariksha (Interrogation-Based Diagnosis)
🗣 Step 1: Patient’s Chief Complaint
- Ask for primary symptoms, onset, and duration.
- Example: “Since when do you feel this pain?” “Is it continuous or intermittent?”
📜 Step 2: Detailed History Taking
- Dietary habits (Ahara Nidana)
- Lifestyle factors (Vihara Nidana)
- Sleep patterns, stress levels, emotions
- Family history of chronic diseases
💬 Step 3: Dosha-Specific Questioning
- Vata: “Do you experience gas, bloating, or insomnia?”
- Pitta: “Do you feel excessive heat, anger, or acidity?”
- Kapha: “Do you feel sluggish, have excessive mucus, or weight gain?”
📊 Clinical Benefit: Identifies root causes and allows personalized treatment.
Final Clinical Decision-Making Based on Trividha Pariksha
| Examination Method | Findings | Probable Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| Darshana | Yellow eyes, skin itching | Jaundice (Pitta Vikara) |
| Sparshana | Cold hands, dry skin | Vata Disorder (Arthritis) |
| Prashna | Acid reflux, burning chest | Hyperacidity (Pitta Prakopa) |
Key Takeaways for Practitioners
✅ Trividha Pariksha provides a rapid, non-invasive diagnostic approach.
✅ Combining all three ensures a holistic understanding of the patient’s condition.
✅ Modern diagnostics (like lab tests, imaging) can be integrated for confirmation.
✅ This structured flowchart improves efficiency in clinical practice.